
It is generally stored in interim storage facilities, where within just forty years its radioactivity levels decrease to one-thousandth of the level.įinally, the potential for disasters such as Chernobyl and Fukushima is a constant concern when considering nuclear power. The nuclear industry produces 34,000m³ of high-level waste globally a year, but counter to what many people believe, it does not take forever to degrade. But 97% of the waste produced is considered low- or intermediate-level waste, and as such is easily disposed of. However unlike other waste streams as it is radioactive. Nuclear plants, like all thermal generation, produce waste. A similar story is true around the world, with reactors often coming in over budget and delayed.

While the running cost over seven years is itself more than the 2019 budget for the Department of Energy’s entire nuclear technology development program, which sits at $740m. This is much more than the initial $3.5bn estimate given by Idaho National Laboratory head Kemal Pasamehmetoglu. A recent versatile test reactor (VTR) project in Idaho is estimated to initially cost between $3.9 and $6bn and $550-850m every year for seven years. However, the initial cost of building a nuclear plant is steep. Unlike wind and solar, nuclear is a consistent, reliable source of energy, which can run uninterrupted for up to a year. Once a nuclear plant is up and running, the electricity it produces is inexpensive due to the low cost of uranium. In this compartment, it becomes steam that is used to powers a turbine.Īs nuclear power does not need to burn anything to create steam it does not emit greenhouse gases like methane or CO 2. Secondly, pressurised water reactors (PWR), which heat up water to close to boiling point before this water is pumped into a separate supply of water. There are two standard types of nuclear reactor, firstly boiling water reactors (BWR), which simply heat up water until it boils to spin turbines and generate electricity. Meanwhile, the released heat causes water within the reactor to boil, which in turn creates the steam that powers the turbines, which powers the generators to make electricity. The neutrons hit other uranium atoms causing them to split, continuing the cycle.
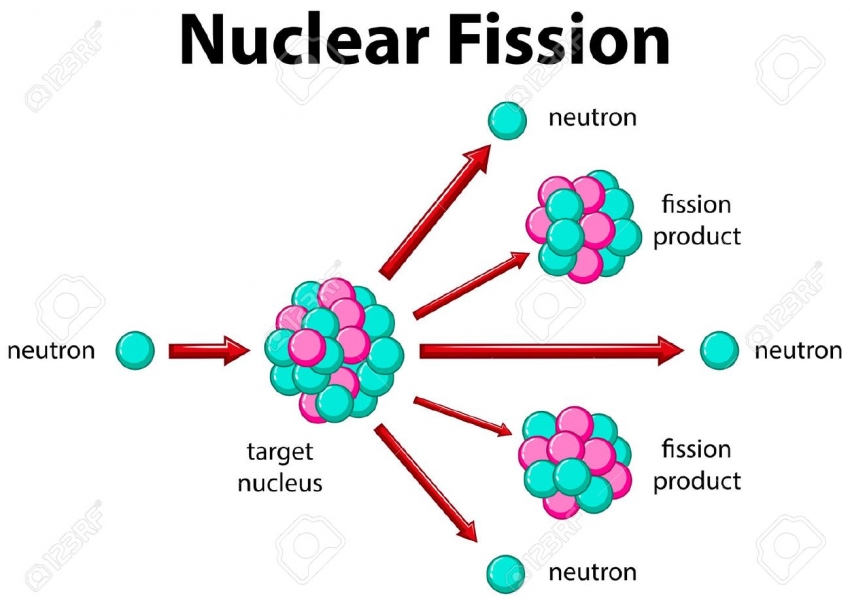
Thanks to nuclear fission, heat and neutrons are released from uranium as the atoms split. These pellets are generally stacked into 12-foot metal fuel rods, which are grouped together in bundles that are called fuel assemblies. Uranium fuel is formed into pellets, one of which can produce as much energy as one tonne of coal, three barrels of oil or 17,000 cubic feet of natural gas. In a nuclear plant, uranium atoms are split in a process called fission, which requires low-enriched uranium fuel. Nuclear plants are different to energy plants such as coal and natural gas, because despite being a thermal generation process they do not need to burn anything to create steam. How does a nuclear power station work exactly? And what are the benefits and perils of nuclear power? How nuclear energy is made
#Fission meaning in tamil download
Please check your email to download the Report.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
